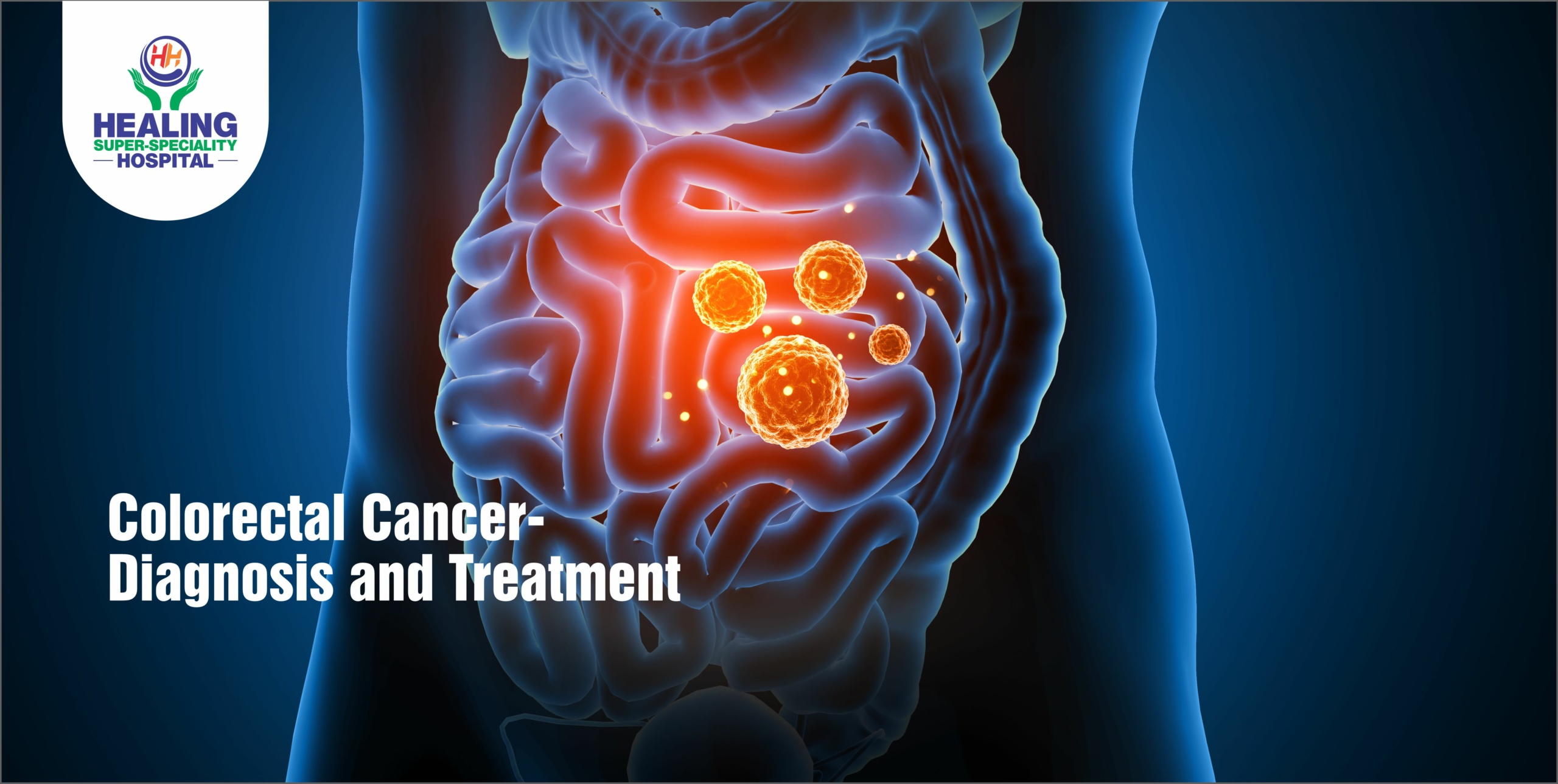
The colon is situated at the end of the digestive tract. Colorectal cancer (colon cancer) starts in the large intestine or colon and generally begins as benign clusters of cells, also known as polyps that can be seen on the inside of the colon. After a period of time, certain polyps can become cancerous leading to colorectal cancer.
Since polyps do not produce any major symptoms, it is important to get regular screening done for colorectal cancer as a preventive strategy. However, if one still gets affected by colorectal cancer, there are numerous treatment options available such as: chemotherapy, surgery, drug treatments, radiation therapy and immunotherapy etc.
When it comes to colon cancer, look for symptoms such as change in bowel habits, blood in stools, rectal bleeding, abdominal discomfort that lingers on, tiredness or unexplained weight loss. However, it is likely that you will not have any symptoms during the initial stages of colorectal cancer.
Certain risk factors for colon cancer include: chronic inflammatory intestinal diseases, family history of colon cancer, older age, previous history of colon cancer or polyps, family history of colorectal cancer, lesser physical activity, excessive consumption of alcohol or increased smoking etc.
Diagnostic tests for colon cancer include: Colonoscopy (using a scope to look at the inside of your colon). It is important to note that blood tests cannot help in determining if you have colon cancer. But your specialist doctor can look for certain chemicals in your blood that are produced during colon cancer. Kidney and liver function tests are also helpful in providing indicators about your overall health. In case colon cancer has been diagnosed, you will be required to undergo imaging procedures such as chest, pelvic and abdominal CT scans.
Treatment options for colon cancer depend on the stage and location of your cancer. For early stage cancer, minimally invasive surgery is a suitable option. These include:
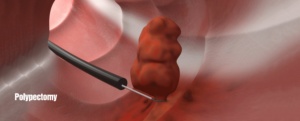
- Polypectomy: It involves removing polyps during colonoscopy at very early stage of the cancer.
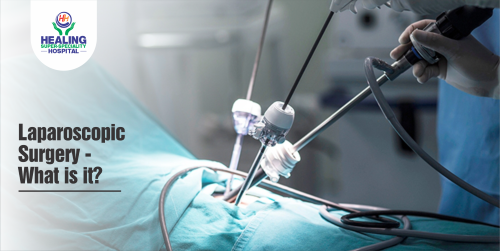
- Laparoscopic surgery: Certain polyps cannot be removed during colonoscopy and therefore, laparoscopic surgery is done to get rid of them.
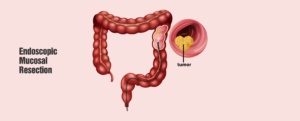
- Endoscopic mucosal resection: This procedure is used for removing larger polyps and a small portion of the inner lining of the colon.
For advanced stage colon cancer, your surgeon can advise you to undergo either of the following:
- Partial colectomy: The part of the colon containing the cancer is removed along with some normal tissue near the cancerous region. The healthy parts of the colon and rectum are then reconnected by the surgeon.
- Ostomy: This procedure involves creating an opening in the abdomen for the waste to leave your body. The stools are eliminated in a bag that is fitted properly over the opening. Ostomy can be temporary (to allow your colon and rectum heal after surgery) or permanent, depending on the condition of the patient.
- Removal of lymph node: Sometimes, lymph nodes situated near the colon are also removed to test for cancer.
If the disease has progressed even further, you will need to undergo chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted drug therapy or immunotherapy as recommended by your doctor.
FOR MORE INFORMATION AND APPOINTMENT CALL:
+0172-5088883, +91 9464343434