Open-heart surgery which is also known as cardiac surgery, is a complex procedure performed to treat various heart conditions. It involves accessing the heart through a large incision in the chest, allowing surgeons to operate on the heart and its major blood vessels. Although it is a major surgery with potential risks, it has saved countless lives and continues to be an important treatment option for certain cardiac conditions. We, at Healing Hospital, the Best heart specialist hospital in Chandigarh are keen to provide you with the best healthcare services whether it is heart health or joints and bones health.
In this blog, we will explore the procedure, risks and recovery associated with open-heart surgery as explained by the Best cardiologist in Chandigarh. So, let’s take a look:
Procedure for the Open Heart Surgery
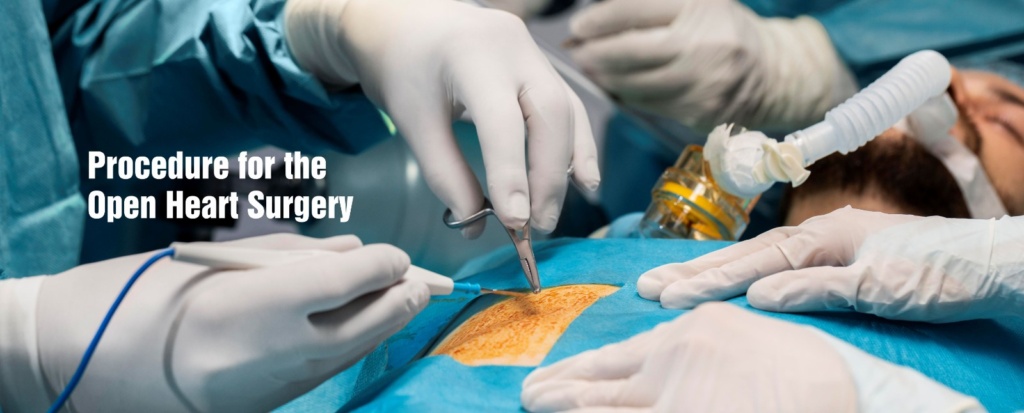
Open-heart surgery typically follows a systematic process involving several stages. Here, we will explain every stage step by step-
Anesthesia: Before the surgery begins, the patient is placed under general anesthesia, which ensures they are asleep and pain-free throughout the procedure of open heart surgery.
Incision: The surgeon makes an incision in the chest, typically down the middle of the breastbone (sternum), which is also known as a median sternotomy. Sometimes, minimally invasive techniques using smaller incisions can be employed.
Cardiopulmonary Bypass (CPB): To allow the surgeon to work on the heart, a heart-lung machine is connected to the patient. The machine takes over the functions of the heart and lungs, circulating oxygenated blood throughout the body.
Opening the heart: The surgeon then opens the pericardium (the protective sac around the heart) to access the heart and perform the necessary repairs or procedures. This may involve coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), valve repair or replacement, atrial or ventricular septal defect repairs, or other interventions specific to the patient’s condition.
Closing the incision: After the necessary repairs are completed, the surgeon closes the incision with sutures or staples. Temporary pacing wires may be placed near the heart to regulate heart rate during the initial recovery phase.
Risks of the Open Heart Surgery
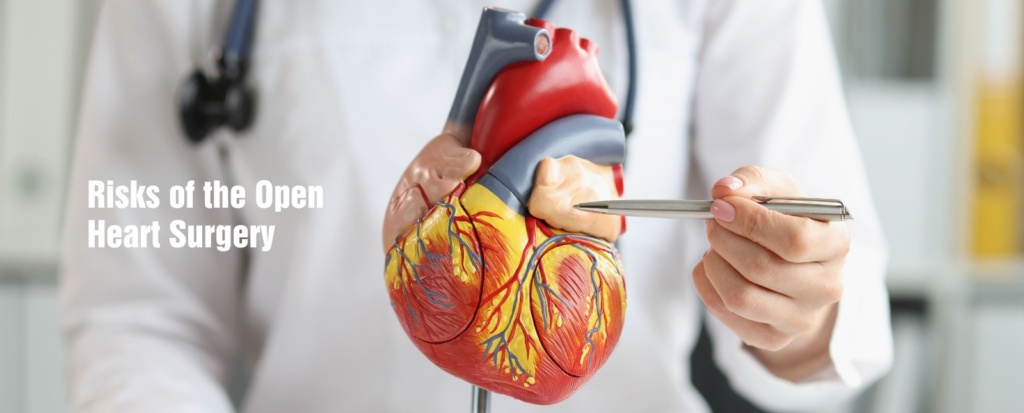
Open-heart surgery carries certain risks, as it is a major surgical procedure involving the heart. Some potential risks include:
Infection: There is a risk of infection at the surgical site or in the bloodstream during the open heart surgery. Strict sterile protocols are followed to minimize this risk.
Bleeding: Surgery may cause excessive bleeding, requiring blood transfusions. Close monitoring and appropriate measures are taken to manage bleeding.
Blood clots: During and after surgery, blood clots can form in the legs or lungs, leading to complications. Medications are administered to prevent clot formation.
Stroke: There is a small risk of stroke during open-heart surgery due to the manipulation of blood vessels or dislodgement of clots.
Arrhythmias: Heart rhythm disturbances may occur after surgery, requiring temporary or permanent pacing.
Lung problems: Due to the use of the heart-lung machine, lung-related issues like fluid accumulation or infection can arise.
Recovery Phase
Recovery from open-heart surgery is a gradual process, and the timeline may vary depending on the individual and the specific procedure performed. Here are some general things you need to know about the recovery period:
Intensive Care Unit (ICU): After surgery, patients are closely monitored in the ICU for a day or more. Vital signs, heart function, and other parameters are closely observed.
Hospital stay: The length of hospitalization varies but typically lasts for about 5 to 7 days. During this time, the medical team manages pain, monitors healing, administers medications, and initiates physical therapy.
Rehabilitation: Once discharged, a structured cardiac rehabilitation program may be recommended. This program helps patients regain strength, improve cardiovascular fitness, and adjust to lifestyle changes to promote long-term heart health.
Medications: Patients are prescribed medications, such as blood thinners, beta-blockers, or statins, to manage heart function, prevent clotting, and control cholesterol levels.
Lifestyle changes: To optimize recovery and maintain heart health, patients are advised to make lifestyle modifications. These may include a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, smoking cessation, weight management, and stress reduction as well.
In a Nutshell
Open-heart surgery is a complex and life-saving procedure used to treat various heart conditions. While it carries risks, the advances in surgical techniques and post-operative care have significantly improved outcomes. The procedure, risks, and recovery associated with open-heart surgery require careful consideration and individualized treatment plans. If you or someone you know is undergoing open-heart surgery, it is important to have open communication with the medical team to understand the specifics of the procedure, address concerns, and support the recovery process.